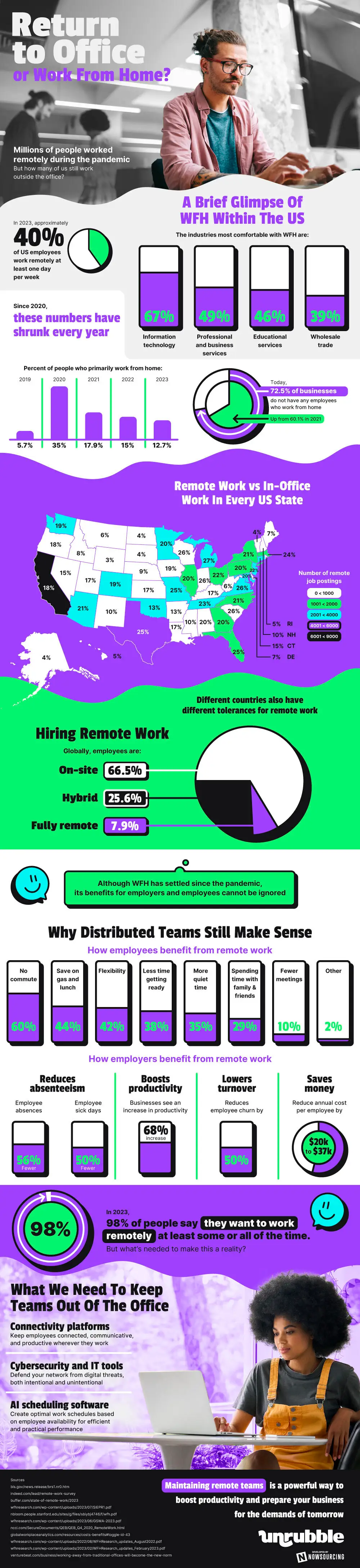
The landscape of remote work in the United States has evolved significantly since the pandemic. In 2024, the trends paint a comprehensive picture of this shift. Initially, remote work was an emergency response, but it has since transformed into a new normal for millions.
As of 2023, about 40% of United States employees worked remotely at least once weekly. Leading the remote work trend are sectors like Information Technology (67%), Professional and Business Services (49%), Educational Services (46%), and Wholesale Trade (39%). However, these figures represent a downtrend from the peak in 2020, when 35% worked primarily from home, dropping to 12.7% in 2023. Remarkably, 72.5% of businesses reported no remote workers in 2023, an increase from 60.1% in 2021.
State-wise, Michigan tops with 27% of its workforce working remotely. States like Wyoming, at the lower end, have just 3%. This variance across states highlights the diversity in work culture and infrastructure.
Globally, the majority of the workforce remains on-site (66.5%), with hybrid (25.6%) and fully remote (7.9%) models also present. Despite the stabilization of remote work, its advantages are undeniable. Employees enjoy benefits like no commute (60%), saving on expenses (44%), and enhanced flexibility (42%). Employers, on the other hand, see reduced absences (56%), decreased sick days (50%), and increased productivity (68%).
In 2023, a staggering 98% of individuals preferred some form of remote work. To sustain this, businesses need robust connectivity platforms, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence-driven scheduling tools. These technologies are crucial for maintaining productive remote teams and positioning businesses for future success.
SME Paid Under